Abstract
Introduction:
Advances in chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy have yielded complete remission (CR) rates in relapsed/refractory B-ALL (rrB-ALL) of 70-95%. However, disease recurrence after CD19 or CD22 CAR therapy is greater than 50% at 1 year, and approximately half of recurrences are due to antigen escape. To reduce antigen escape and optimize the durability of remission, we sought to design a CAR T cell product with dual specificity that is capable of simultaneously targeting both CD19 and CD22. Preclinical testing of our bi-specific CAR showed a preference for signaling through CD22 over the CD19 CAR. In contrast, dual transduced T cells signaled through both the CD19 and CD22 CAR with lytic activity and cytokine production similar to single transduced CAR T cells of the same specificity. Therefore, we opted to move forward with dual transduced T cells for clinical use. We are currently testing SCRI-CAR19x22v1 in PLAT-05 (NCT03330691), a phase 1 clinical trial for pediatric and young adult patients with CD19+CD22+ rrB-ALL, with the primary objectives to determine the feasibility of manufacturing products with dual specificity, to assess the safety of the cryopreserved product infusion, and to describe the full toxicity profile.
Methods:
Subjects undergo apheresis, after which the CD4 and CD8 T cell subsets are immunomagnetically selected and seeded at a prescribed ratio for co-culture in a closed-system G-Rex bioreactor. Following anti-CD3xCD28 bead stimulation, T cells are transduced with two separate SIN lentiviral vectors that direct the expression of a CD19-specific FMC63scFv:IgG4hinge:CD28tm:4-1BB:ζ CAR with an Her2tG tag and expression of a CD22-specific m971scFv:IgG4hinge:CH2(L235D)-CH3:CD28tm:4-1BB:ζ CAR with an EGFRt tag, creating three distinct populations of CAR T cells (anti-CD19, anti-CD22, and anti-CD19x 22). Transduced cells are expanded in serum free media formulation with IL-7, IL-15, and IL-21. Following lymphodepleting chemotherapy, cryopreserved products are thawed and infused at the protocol-prescribed dose level. Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) is graded according to Lee et al. (Blood 2014) and is treated according to our early intervention strategy of tocilizumab and dexamethasone for persistent, mild CRS.
Results:
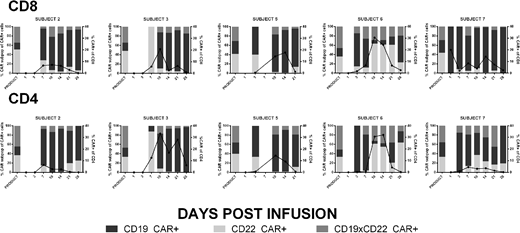
Seven subjects (ages 1-26 yr) with rrB-ALL have been enrolled with 4 treated at dose level 1 (1 x 106 CAR T cells/kg) and 3 treated at dose level 2 (3 x 106 CAR T cells/kg). The mean culture time was 7.9 days (range 7-11) and subjects received infusions with a mean CD8:CD4 ratio of 1.7 (range 0.2 - 3.1). CD8 CAR composition, on average, consisted of 21.6 % CD19 CAR, 37.8 % CD22 CAR, and 40.6 % CD22xCD19 CAR T cells. CD4 CAR composition, on average, consisted of 25.8 % CD19 CAR, 30.6 % CD22 CAR, and 43.6 % CD22xCD19 CAR T cells (Figure). Peak engraftment occurred between days 7 and 14 for all patients and was predominantly composed of the CD19 CAR population with median peak values for CD19 CAR, CD22 CAR, and CD19xCD22 CAR T cell populations of 9.1%, 1.2%, and 2.4%, respectively. A CR was achieved in 5/7 (71%) subjects by day 21, 4 of which were minimal residual disease negative. The two subjects without a CR did not exhibit evidence of CAR T cell engraftment; one had previously received CD19 CAR T cells, and the other had progressive disease and pursued alternative therapy at day 10. Therapy was well tolerated with no dose limiting toxicities. CRS occurred in 5 subjects (Grade 1) with 2 of these subjects experiencing mild neurotoxicity (Grade 1). Four subjects received tocilizumab +/- dexamethasone, and two of these received multiple doses of dexamethasone.
Conclusions:
Preclinical testing showed superior efficacy against both CD19 and CD22 when using two separate CARs and dual transduction, compared to a single bi-specific CAR. Preliminary analysis of PLAT-05 supports feasibility of product manufacturing, and toxicity and response rates that are consistent with the reported CD19 CAR T cell experience. While the infused SCRI-CAR19x22v1 products consist of a near-uniform distribution of the 3 distinct populations, we observed selective in vivo expansion of the CD19 CAR T cell population. Further investigation is required to understand the mechanism of CD19 CAR dominance in vivo. Continued accrual of subjects is ongoing to further assess the impact of dual antigen targeting on the prevention of antigen escape and the potential to provide a more durable remission.
Park:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Jensen:Juno Therapeutics, Inc.: Consultancy, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal